|
|
|---|
Sunday, March 6, 2011

Beta hemolytic - complete lysis of red blood cells 
Human red blood cells, T-lymphocyte and platelets (c) Dennis Kunkel
Alpha hemolytic - partial lysis of red blood cells, producing a greenish 
Non-phagocytosed RBCs are removed, followed by lysis of phagocytes and 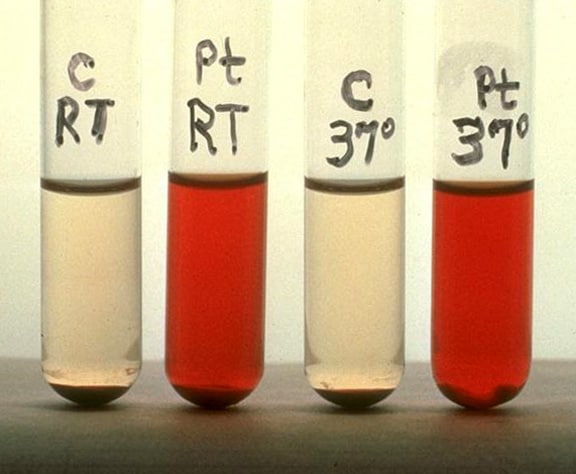
Here is a PNH patient's (Pt) red blood cells lysed by normal serum at room 
in cell lysis and agglutination. Beyond the obvious detrimental effects 
erythrocytes (red blood cells 
Nocturnal haemolysis
effected when compared to the incorporation of an RBC lysis step.
with the addition of an RBC lysis step (Figure 1 and data not shown).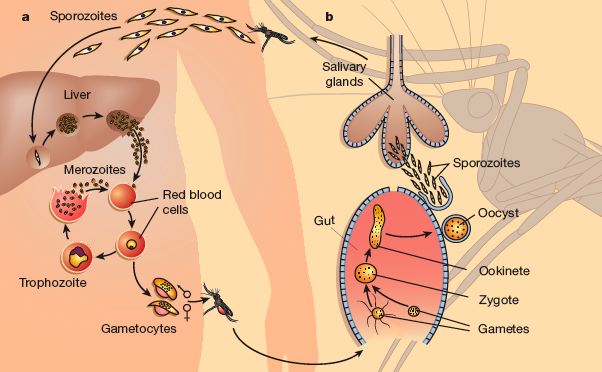
After lysis of hepatocytes, merozoytes spread into the bloodstream and red 
were obtained by homogenization of the spleen and lysis of RBC.
Model for regulation of perforin-mediated lysis by calreticulin and Chymase 
without Lysing Red Blood Cells
proteins or phospholipases or lecithinases that destroy red blood cells 
In the above diagram, a red blood cell has antigen fixed on its surface to 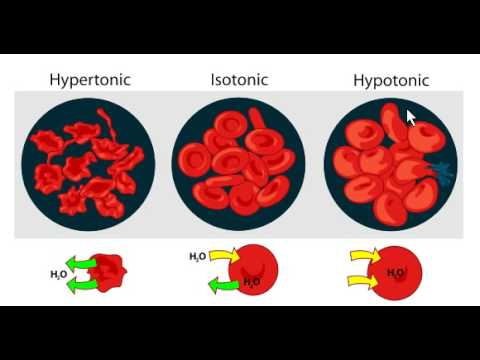
Red Blood Cells in Hypotonic Solution · RBC Lysis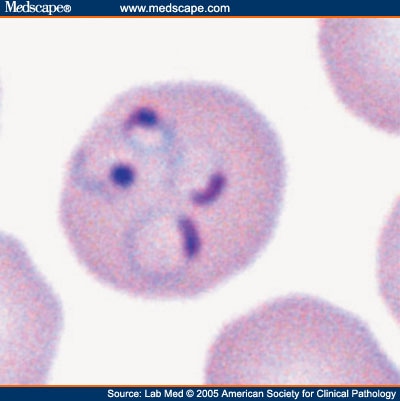
(D) a non-enlarged multiply infected red blood cell with 
on red blood cells to cause lysis. At the stage shown, these bites may 
The residual RBC in the Purecell Select System samples without RBC reduction













